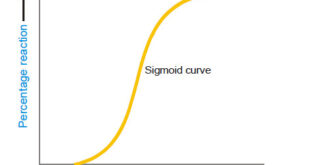
– In this topic, we will discuss Autocatalysis, Catalytic poisoning and Negative Catalysis. Catalytic poisoning – Very often a heterogeneous catalyst in rendered ineffective by the presence of small amounts of impurities in the reactants. – A substance which destroys the activity of the catalyst to accelerate a reaction, is …
Read More »NMR – Theory of Magnetic Nuclear Resonance
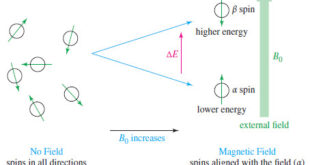
Introduction to NMR – Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the most powerful tool available for organic structure determination. – Like infrared spectroscopy, NMR can be used with a very small sample, and it does not harm the sample. – The NMR spectrum provides a great deal of information about …
Read More »Characteristics of Catalytic Reactions
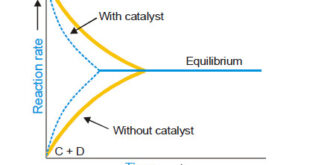
– In this topic, we will discuss general Characteristics of Catalytic Reactions and Promoters. General Characteristics of Catalytic Reactions – Although there are different types of catalytic reactions, the following features or characteristics are common to most of them. (1) A catalyst remains unchanged in mass and chemical composition at …
Read More »Fragmentation Patterns in Mass Spectrometry
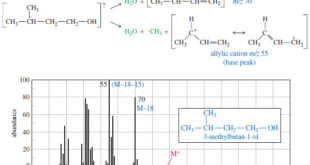
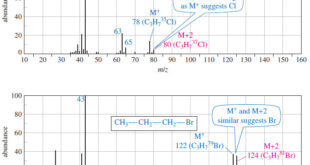
– In this topic, we will discuss the Fragmentation Patterns in Mass Spectrometry. Fragmentation Patterns in Mass Spectrometry – In addition to the molecular formula, the mass spectrum provides structural information. – An electron with a typical energy of 70 eV (6740 kJ mol or 1610 kcal mol) has far …
Read More »Catalysis: Types of Catalysis
– In this topic, we will discuss the Catalysis and The types of catalysis : Homogeneous catalysis – Heterogenous catalysis. What is Catalysis? – Berzelius (1836) realised that there are substances which increase the rate of a reaction without themselves being consumed. – He believed that the function of such …
Read More »Collision theory of Reaction rates
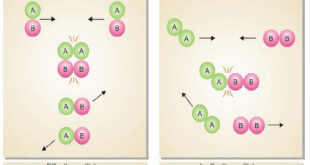
Collision theory of Reaction rates – According to collision theory, a chemical reaction takes place only by collisions between the reacting molecules. However, not all collisions are effective. – Only a small fraction of the collisions produce a reaction. – The two main conditions for a collision between the reacting …
Read More »Determination of the Molecular Formula by Mass Spectrometry
Determination of the Molecular Formula by Mass Spectrometry – we can Determine the Molecular Formula by Mass Spectrometry and we will discuss : (A) High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (B) Use of Heavier Isotope Peaks (A) High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry – Although mass spectra usually show the particle masses rounded to the nearest …
Read More »Mass Spectrometry : Introduction
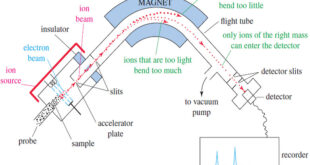
Mass spectrometry (MS) provides the molecular weight and valuable information about the molecular formula, using a very small sample. Introduction to Mass Spectrometry – Infrared spectroscopy gives information about the functional groups in a molecule, but it tells little about the size of the molecule or what heteroatoms are present. …
Read More »How to determine the order of reaction?
Determination of the order of reaction – There are at least four different methods to determine the order of reaction as follows: Using integrated rate equations Graphical method Using half-life period The Differential method Ostwald’s Isolation method (1) Using integrated rate equations – The reaction under study is performed by …
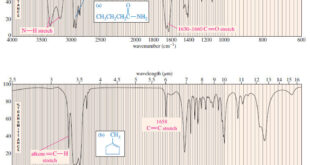
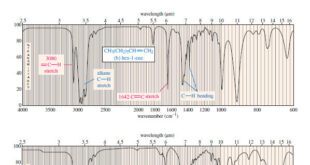
Read More »Characteristic Absorptions of Carbonyl Compounds
– In this subject, we will talk about Characteristic Absorptions of Carbonyl Compounds such as Ketones, Aldehydes, Amines, and Acids. Characteristic Absorptions of Carbonyl Compounds – Because it has a large dipole moment, the C=O double bond produces intense infrared stretching absorptions. – Carbonyl groups absorb at frequencies around 1700 …
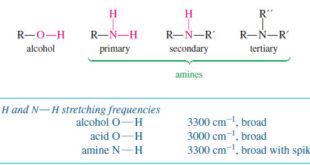
Read More »Characteristic Absorptions of Alcohols and Amines
– In this topic, we will discuss the Characteristic Absorptions of Alcohols and Amines by examples. Characteristic Absorptions of Alcohols and Amines – The O-H bonds of alcohols and the N-H bonds of amines are strong and stiff. – The vibration frequencies of O-H and N-H bonds therefore occur at …
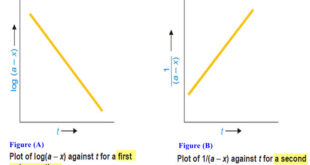
Read More »Second order reaction
Second order reaction – Let us take a second order reaction of the type 2A ⎯⎯→ products – Suppose the initial concentration of A is a moles liter–1. – If after time t, x moles of A have reacted, the concentration of A is (a – x). – We know …
Read More »Hydrocarbons: Infrared Spectroscopy of Hydrocarbons
Infrared Spectroscopy of Hydrocarbons – Hydrocarbons contain only carbon–carbon bonds and carbon–hydrogen bonds. – An infrared spectrum does not provide enough information to identify a structure conclusively (unless an authentic spectrum is available to compare “fingerprints”), but the absorptions of the carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen bonds can indicate the presence of …
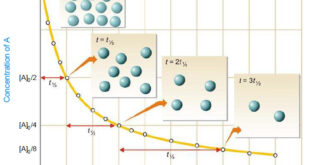
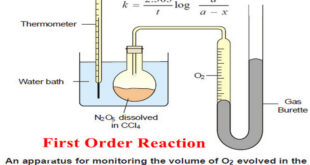
Read More »First Order Reaction -Examples and Solved problems
First order reaction – Let us consider a first order reaction: A → products – Suppose that at the beginning of the reaction (t = 0), the concentration of A is a moles liter–1. – If after time t, x moles of A have changed, the concentration of A is …
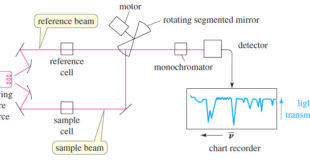
Read More »IR Spectrum – Measurement of the IR Spectrum
– In this subject, we talk about how to Measure the IR Spectrum. Measurement of the IR Spectrum – Infrared spectra can be measured using liquid, solid, or gaseous samples that are placed in the beam of infrared light. – A drop of a liquid can be placed as a …
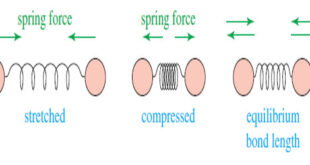
Read More »Molecular Vibrations : IR spectrum
– In this subject we talk about Molecular Vibrations as introduction to understand IR spectrum Molecular Vibrations – Before discussing characteristic infrared absorptions, it’s helpful to understand some theory about the vibrational energies of molecules. – The following drawing shows how a covalent bond between two atoms acts like a …
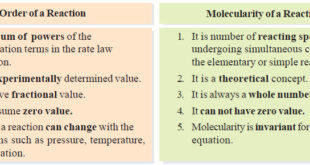
Read More »Molecularity of a reaction
– we will discuss the Molecularity of a reaction and the Differences Between Order and Molecularity. Molecularity of a reaction – Chemical reactions may be classed into two types : (a) Elementary reactions (b) Complex reactions – An elementary reaction is a simple reaction which occurs in a single step. …
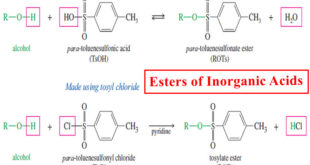
Read More »Inorganic Esters – Esters of Inorganic Acids
Esters of Inorganic Acids – In addition to forming esters with carboxylic acids, alcohols form inorganic esters with inorganic acids such as nitric acid, sulfuric acid, and phosphoric acid. – In each type of ester, the alkoxy (-OR) group of the alcohol replaces a hydroxyl group of the acid, with …
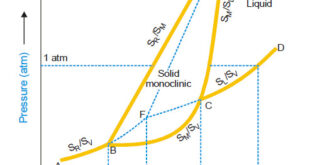
Read More »Sulphur system – Phase diagram of Sulphur
The Sulphur system – Sulphur system is a one-component, four-phase system. – The four phases are: (a) Two solid polymorphic forms : Rhombic Sulphur (SR) Monoclinic Sulphur (SM) (b) Sulphur Liquid (SL) (c) Sulphur Vapour (SV) – All the four phase can be represented by the only chemical individual (sulphur) …
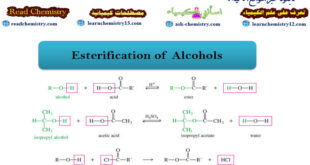
Read More »Esterification of Alcohols
– In this subject we will talk about the Esterification of Alcohols. What are Alcohols? – Alcohols are organic compounds containing hydroxyl (-OH) groups. – They are some of the most common and useful compounds in nature, in industry, and around the house. – The word alcohol is one of …
Read More » Read Chemistry
Read Chemistry